How Do Kettle Lakes Form? Nature’s Sculpting Secrets
Have you ever marveled at the serene beauty of a kettle lake, nestled amidst lush landscapes? These natural wonders, with their tranquil waters and unique shapes, seem like nature’s own masterpieces.
But have you ever wondered how these intriguing bodies of water came to be? Understanding the formation of kettle lakes is like uncovering a fascinating story written by time and nature itself. As you delve into the details, you’ll discover how glaciers, ice chunks, and the gradual dance of nature’s elements play pivotal roles in crafting these scenic lakes.
This exploration promises to satisfy your curiosity and deepen your appreciation for the natural world, making it impossible to look at kettle lakes in the same way again. Ready to uncover the secrets behind these captivating water bodies? Let’s dive in!
How Do Kettle Lakes Form?
Glacial Retreat And Lake Formation
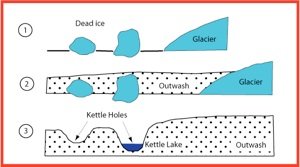
Glaciers leave behind unique landscapes. As they melt, large chunks of ice can get buried in sediment. These chunks eventually melt, forming kettle lakes. These lakes are typically small, circular, and scattered across glacial plains.
Glacial retreat and lake formation is a captivating geological process that has shaped many landscapes around the world. As glaciers slowly recede, they leave behind kettle lakes, which are unique water bodies formed in the depressions created by melting ice. These lakes are not only fascinating to study but also offer a glimpse into the Earth’s climatic past.
What Causes Glacial Retreat?
Glacial retreat occurs when the accumulation of snow is less than the melting rate of the glacier. This can be due to rising temperatures or changes in precipitation patterns. As the glacier retreats, it leaves behind a variety of landforms, including valleys, moraines, and kettle lakes.
How Do Kettle Lakes Form?
Kettle lakes form when large chunks of ice break off from a retreating glacier and become buried in sediment. As these ice blocks melt, they create depressions in the Earth’s surface. These depressions eventually fill with water, forming kettle lakes. You can spot these lakes in areas that have experienced glaciation, like parts of North America and Europe.
Why Are Kettle Lakes Important?
Kettle lakes serve as natural reservoirs and habitats for diverse ecosystems. They can also be important indicators of historical climate changes. Studying these lakes provides valuable insights into past glacial movements and environmental conditions.
What Can You Learn From Kettle Lakes?
Kettle lakes offer a unique opportunity to understand glacial history and its impact on landscapes. You can explore how these lakes influence local biodiversity and water systems. Do you think they reveal clues about past climates? How might this information help us understand current environmental changes?
How To Observe Kettle Lakes?
When visiting areas with kettle lakes, pay attention to the surrounding terrain. Notice the distinct circular shapes and the vegetation around them. These lakes can often be found in clusters, hinting at the extensive glaciation that once occurred. Whether you’re hiking or driving through glacial regions, kettle lakes are a reminder of nature’s ability to transform landscapes over time.
Ice Blocks And Depression Creation
Kettle lakes form through ice blocks left by retreating glaciers. These ice blocks melt, creating depressions. Water fills these depressions, resulting in kettle lakes.
Ice Blocks and Depression Creation Kettle lakes tell a fascinating story of nature’s artistry. These unique lakes are born from the remnants of glaciers. The process involves the intriguing mechanism of ice blocks and depression creation. Imagine a giant ice block left behind by a retreating glacier. As it melts, a depression forms in the ground. This depression, often filled with water, becomes a kettle lake.
Understanding Ice Blocks
Ice blocks are key players in the formation of kettle lakes. They are large chunks of ice that break off from a glacier. As glaciers move, they can leave these massive ice blocks behind. These blocks become isolated from the main glacier. Over time, they slowly melt. This melting plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape.
The Melting Process
As the ice blocks melt, they leave behind depressions. This is the first step in creating a kettle lake. The melting process can take years or even decades. The length of time depends on the size of the ice block. Larger blocks take longer to melt, creating deeper depressions.
Creating Depressions
The melting ice block leaves a significant mark on the land. The depression varies in size and shape. Some depressions are small, while others are vast. Have you ever wondered how these depressions affect the ecosystem? They often become habitats for various species, adding biodiversity to the area.
Filling With Water
Once a depression forms, it can fill with water. This water can come from rainfall, groundwater, or nearby streams. The water accumulation turns the depression into a lake. Have you ever visited a kettle lake? You might have noticed its calm and serene appearance. This tranquility is a result of its unique formation process.
Impact On The Environment
Kettle lakes have a significant environmental impact. They create habitats for plants and animals. These lakes also influence local climate and water tables. Would you consider visiting a kettle lake to observe its beauty and ecological importance? Understanding the formation of kettle lakes through ice blocks and depression creation enhances your appreciation for these natural wonders. Next time you’re near a kettle lake, think about the incredible journey of ice blocks and melting that led to its creation.
Sediment Accumulation And Basin Shaping
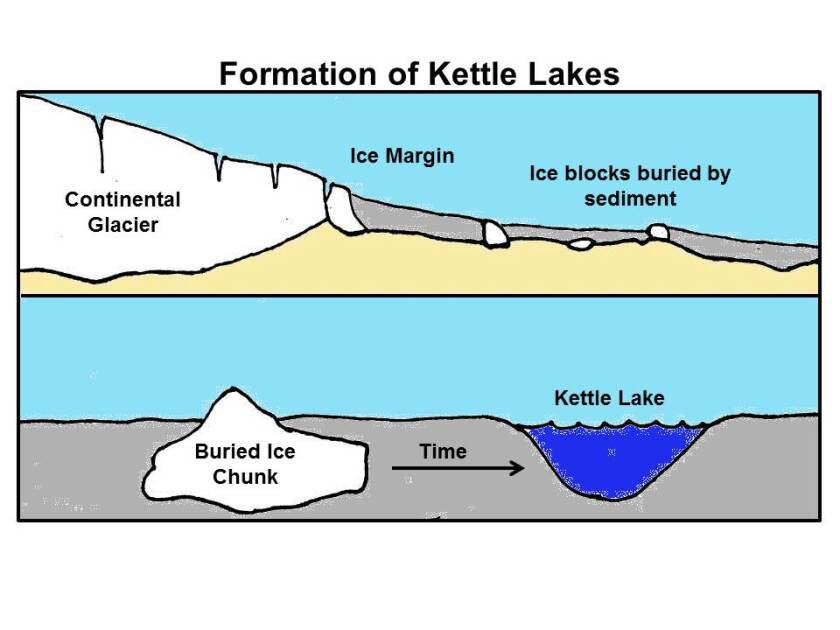
Kettle lakes are unique features shaped by ancient glaciers. Sediment accumulation and basin shaping play crucial roles in their formation. As glaciers retreat, they leave behind blocks of ice buried under sediment. Over time, these ice blocks melt, creating depressions. These depressions, or kettles, gradually fill with water, forming lakes. The process involves complex interactions between sediment and ice. Understanding these interactions helps explain the distinct characteristics of kettle lakes.
Formation Of Sediment Layers
Sediment layers form as glaciers move across landscapes. They pick up rocks, soil, and debris. This material gets deposited over time. Layers of sediment build up, covering ice blocks left behind. These layers protect the ice from melting quickly. The weight of the sediment shapes the basin beneath. This creates the foundation of a kettle lake.
Influence Of Basin Shape
The shape of the basin affects the lake’s size and depth. The ice block’s original size and location determine this shape. If the basin is deep, the lake holds more water. Shallow basins lead to smaller lakes. The surrounding landscape also impacts basin shape. Hills and valleys can direct water flow into the basin. This influences the lake’s final form.
Role Of Water And Vegetation
Water and vegetation play vital roles in shaping kettle lakes. Water fills the basin, forming the lake. Over time, vegetation grows around it. Plant roots help stabilize the soil. This prevents excessive erosion. Vegetation also affects sediment distribution. Some plants trap sediment, changing the lake’s shoreline.
Erosion And Sediment Redistribution
Erosion reshapes the landscape around kettle lakes. Wind and water move sediment, altering the basin. This changes the lake’s appearance over time. Sediment redistribution can fill parts of the lake. This affects its depth and water clarity. Monitoring these changes helps understand lake dynamics.
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Water Filling And Ecosystem Development
Kettle lakes form in depressions left by melting glaciers. As ice blocks melt, they create holes filled with water. These lakes become vital habitats for wildlife, supporting diverse ecosystems.
Kettle lakes are fascinating natural formations with unique origins and vibrant ecosystems. These lakes are formed when blocks of ice, left behind by retreating glaciers, melt and fill depressions in the Earth’s surface. Once the water fills these depressions, a new ecosystem begins to emerge, teeming with life and diversity.
How Water Fills A Kettle Lake
The process starts with glacial retreat. As glaciers move back, they leave behind large chunks of ice. Over time, these ice blocks become buried under sediments. Eventually, the ice melts, creating a depression filled with water. Rainfall and groundwater also contribute to the filling process. This mixture of sources ensures a steady water supply, maintaining the lake over time. These water bodies can vary in size, from small ponds to larger lakes, depending on the size of the original ice block.
Initial Ecosystem Development
Once the lake forms, pioneer species like algae and aquatic plants start to establish themselves. These plants are crucial as they provide oxygen and food sources for other organisms. They lay the foundation for a thriving aquatic community. Birds and insects are often among the first visitors. They bring seeds and other organic materials, enriching the ecosystem. As more species arrive, the food web becomes more complex, supporting a variety of life forms.
Long-term Ecological Succession
Over time, kettle lakes may undergo ecological succession. This is a natural process where ecosystems change and develop gradually. What starts as an open water body might slowly fill with sediments, turning into a marsh or meadow. Do you know how this process benefits the surrounding environment? As these lakes evolve, they create habitats for diverse species, from amphibians to mammals. This transformation highlights nature’s incredible ability to adapt and flourish.
Your Role In Supporting Kettle Lake Ecosystems
Understanding how kettle lakes form and develop can inspire conservation efforts. You can contribute by supporting local conservation initiatives aimed at preserving these unique ecosystems. Small actions, like reducing pollution and promoting awareness, can make a significant difference. Have you ever visited a kettle lake? Observing these natural wonders can deepen your appreciation for their beauty and complexity. Next time you explore one, remember the intricate processes that shaped its existence.
Geographical Distribution And Examples
Kettle lakes are fascinating geological formations. They showcase the Earth’s dynamic processes. These lakes are scattered across various parts of the world. They form unique ecosystems and landscapes wherever they appear. Understanding their distribution helps us appreciate their global significance.
Kettle Lakes In North America
North America hosts many kettle lakes. Most are found in regions once covered by glaciers. The Great Lakes region, including Minnesota and Michigan, is notable. These areas have numerous kettle lakes. They serve as habitats for diverse wildlife. They also offer recreational opportunities for local communities.
Kettle Lakes In Europe
Europe’s landscape also features kettle lakes. Countries like Finland and Sweden have many of them. They dot the terrain, adding to the scenic beauty. These lakes are vital for local biodiversity. They support both plant and animal life, maintaining ecological balance.
Kettle Lakes In Asia
In Asia, kettle lakes appear in northern regions. Russia’s Siberia hosts several examples. These lakes are remnants of the last Ice Age. They play a crucial role in local ecosystems. They provide water sources and habitat for wildlife. Their presence underscores the impact of historical glaciation.
Kettle Lakes In Other Continents
While less common, kettle lakes exist in other continents too. South America’s Andes region has a few. They result from ancient glacial activity. These lakes offer insight into past climatic conditions. In Africa, kettle lakes are rare. Yet, they hold significance for local ecosystems. Each kettle lake tells a story of the Earth’s glacial past.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Credit: www.superiortelegram.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Tell If A Lake Is A Kettle Lake?
A kettle lake forms from melting glaciers, creating a depression filled with water. It usually appears round or oval. Look for steep sides and a deep basin. These lakes often have no inlets or outlets. Kettle lakes are common in glaciated regions.
How Are Kettle Swamps Formed?
Kettle swamps form when ice blocks melt in glacial deposits, creating depressions that fill with water. These depressions become wetlands over time, supporting diverse ecosystems. Kettle swamps are often surrounded by moraines or glacial till, contributing to their unique landscapes.
What Is The Primary Factor That Led To The Formation Of Kettle Lakes In Kettle Lakes Provincial Park?
Glacial retreat primarily led to the formation of kettle lakes in Kettle Lakes Provincial Park. Melting ice blocks left depressions, creating these unique lakes.
Conclusion
Kettle lakes tell a fascinating story of nature’s processes. Formed by melting glaciers, they leave behind unique landscapes. These lakes offer habitats for diverse wildlife. People enjoy their serene beauty and recreational activities. Understanding kettle lakes helps us appreciate Earth’s history.
They remind us of the power and beauty of natural forces. This knowledge enriches our connection with the environment. Observing these wonders can inspire future exploration and learning. Nature’s processes truly shape our world in remarkable ways. Keep exploring these natural treasures and discover more wonders around us.
Read More
- How to Clean the Kettle? Expert Tips for Sparkling Results
- What are the Best Electric Tea Kettles? Top Picks Revealed
- How to Use Cast Iron Tea Kettle: Expert Brewing Tips

Natasha, founder of NatashasKitchenTips.com, shares easy, flavorful recipes and practical cooking tips to help home cooks feel confident in the kitchen. With a passion for simple, delicious meals, she inspires readers to cook with joy and creativity every day.